A function is a block of code that performs a specific task.
Suppose, a program related to graphics needs to create a circle and color it depending upon the radius and color from the user. You can create two functions to solve this problem:
- create a circle function
- color function
Dividing complex problem into small components makes program easy to understand and use.
Types of functions in C programming
Depending on whether a function is defined by the user or already included in C compilers, there are two types of functions in C programming
There are two types of functions in C programming:
- Standard library functions
- User defined functions
Standard library functions
The standard library functions are built-in functions in C programming to handle tasks such as mathematical computations, I/O processing, string handling etc.
These functions are defined in the header file. When you include the header file, these functions are available for use. For example:
The
printf() is a standard library function to send formatted output to the screen (display output on the screen). This function is defined in "stdio.h" header file.
There are other numerous library functions defined under
"stdio.h", such as scanf(), fprintf(), getchar() etc. Once you include "stdio.h" in your program, all these functions are available for use.
Visit this page to learn more about standard library functions in C programming.
User-defined functions
As mentioned earlier, C allow programmers to define functions. Such functions created by the user are called user-defined functions.
Depending upon the complexity and requirement of the program, you can create as many user-defined functions as you want.
How user-defined function works?
#include <stdio.h>
void functionName()
{
... .. ...
... .. ...
}
int main()
{
... .. ...
... .. ...
functionName();
... .. ...
... .. ...
}
The execution of a C program begins from the
main() function.
When the compiler encounters
functionName(); inside the main function, control of the program jumps tovoid functionName()
And, the compiler starts executing the codes inside the user-defined function.
The control of the program jumps to statement next to
functionName(); once all the codes inside the function definition are executed.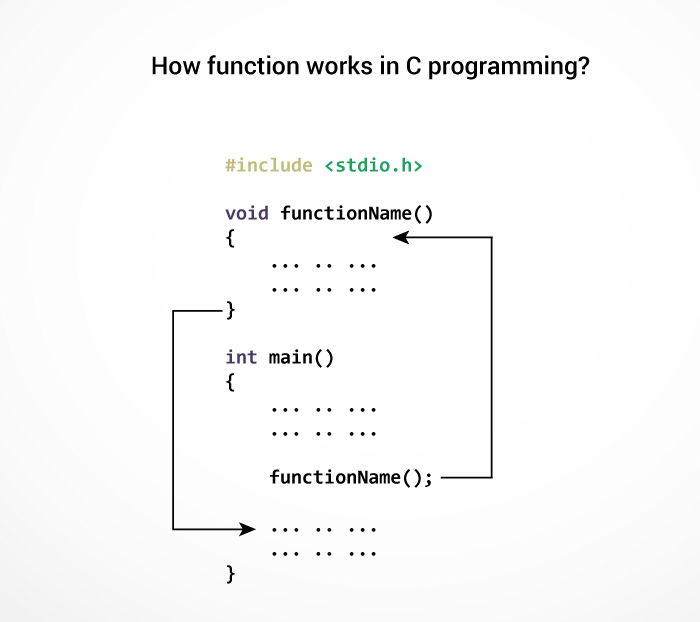
Remember, function name is an identifier and should be unique.
This is just an overview on user-defined function. Visit these pages to learn more on:
- User-defined Function in C programming
- Types of user-defined Functions
Advantages of user-defined function
- The program will be easier to understand, maintain and debug.
- Reusable codes that can be used in other programs
- A large program can be divided into smaller modules. Hence, a large project can be divided among many programmers.
No comments:
Post a Comment